

The tool also works as a modifier so that you can remove or modify these cookies to maintain necessary compliance. The tool is even capable of detecting the often-missed Javascript cookies. As mentioned above, those cookies can be removed by running a database inquiry to make large-scale changes. This includes any lingering YouTube cookies from previously embedded videos. It becomes exceedingly difficult to follow privacy regulations or any cookie laws when you are unaware of what is there.ĬookieScript’s cookie scanner tool will scan your website, and alert you to all cookies that are running. You may or may not be aware of all the cookies running on your site, as many could come from a third party. If you embed video to your website and have European visitors, it’s a shift necessary to maintain GDPR compliance. Large websites such as Kahn Academy are using this technique to remove the tracker.
Embedded video website code#
Instead, you can go to the database, run a query, and replace the code with all the “no cookie” embed code. You don’t have to re-do all the code on the videos currently embedded into your site. This addition is what is supposed to prevent the videos watched from your website from influencing users’ browsing experience on YouTube. Note that the “section has been added to the privacy mode version. Below is an example of what the code might look like before and after. When you check the box, the code automatically adds the “no cookie” code to the domain, removing the tracker and making the embed GDPR compliant. When you go to imbed the video from YouTube, you can click on “Enable privacy-enhanced mode” toward the bottom of the screen. The way for users to maintain compliance with this issue is straightforward. You can read more about the role of cookies in GDPR compliance. Your company may be collecting and storing personal data through third-party cookies without even knowing it. The GDPR regulates how that personal data can be collected or used by private organizations. This shift in policy brings hosting YouTube videos on your site using this option, a GDPR compliant practice.Īccording to the GDPR, if cookies can be used to identify a person, they are considered personal data.
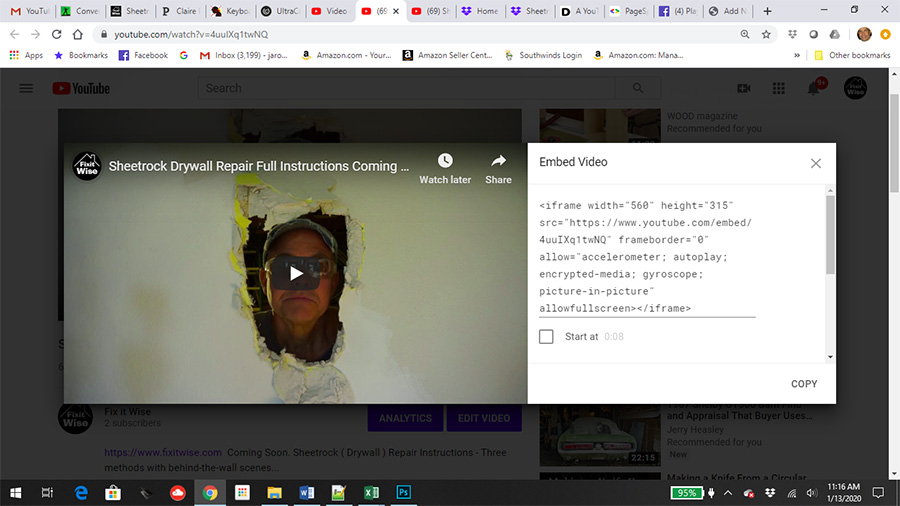
This cookie is what allows them to tailor the next videos that you might see to previous related searches, or videos watched.īut this practice violates the European Union’s GDPR, which requires the user to provide consent for any tracking cookie that is used. Historically, YouTube has used a tracking cookie in this process to personalize the viewing experience for users.

It pulls the video from its source, allowing users to see the video without needing to host it on your site. Essentially, you are using a small snippet of code on your website that displays the video to users. How Embedded YouTube Videos WorkĪs mentioned above, embedded YouTube videos allow websites to incorporate video into their site without slowing down site speed. Generally, website users who click on the video from your website have not consented to this tracker like they would if they directly visited YouTube.Īs of recently, YouTube launched a GDPR-compliant solution to this issue, however, that allows users to imbed videos without the attached cookie. This can cause some complications when it comes to General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) compliance. In other words, when you embed a video, you are inviting third-party cookies onto your site. YouTube by default sets a tracking cookie for marketing purposes. While this simple strategy makes using video infinitely easier, it also comes with a downside when it comes to privacy regulations. It’s the simplest way to incorporate video without drastically impacting site speed. Businesses, media outlets, and bloggers commonly embed YouTube videos into their websites.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
